Melasma
Melasma is a skin condition that often presents as pigmentation patches on different face areas. It is usually identified as brown patches on the cheeks, nose, and forehead that often occur with pregnancy or long-term sun exposure and is typically seen in women. While good skincare control and sun protection are essential for controlling melasma, sometimes it requires more intensive treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion depending on the severity of the individual symptoms. Fortunately, you can manage your melasma by utilizing procedures that break up the pigment clusters and reveal healthier skin underneath, resulting in a luminous and smooth complexion.

What is Melasma?
Melasma is a common form of hyperpigmentation, appearing as flat patches with varying shades of gray or brown. These usually appear on the forehead, cheeks, nose, and the area where it appears, across the length of the upper lip, such as a “melasma mustache”. Also referred to as chloasma in some cases, melasma can reach both epidermally (the skin’s surface) and dermally (under the skin). Melasma affects mostly women and can be triggered by a sudden hormone change or exposure to UV radiation. With more active melanin-producing cells, those with medium to dark (Fitzpatrick IV-VI) complexions are at an increased risk of developing melasma. However, those with fair complexions may still fall victim.
Treatment options range from topical medications like hydroquinone to more intensive therapies including laser therapy, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion. Treatments are more challenging when addressing pigmentation that goes deeper into the skin layer. Wear protective headgear such as hats or scarves when exposed to the sun to reduce your risk of developing melasma. Also, you should always apply sunscreen with a minimum SPF-30 before going out in the sun as it helps block the UV rays that could worsen melasma. Additionally, be aware that medications, such as hormonal medications can aggravate melasma formation.
Common Types of Melasma
Melasma can occur on the skin’s surface (in the epidermis) or deep underneath it (in the dermis), or both. Individuals with medium to dark complexions are particularly vulnerable to melasma due to increased melanin-producing cells; however, those with lighter complexions are not immune. Although deeper melasma may be more difficult to treat, various treatment options are available depending upon severity.
Epidermal
Epidermal melasma is a common skin condition caused by a buildup of the dark pigment melanin in certain areas of the skin. While it can affect any body part, it most commonly appears on the face. Characterized by brown and gray discoloration patches, epidermal melasma can be extremely distressing cosmetically. Fortunately, this condition can often be managed effectively with specific treatment options including topical skincare products, light and laser treatments, microdermabrasion, and more. It is important to visit a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for you and monitor and adjust your treatment plan regularly for optimal results.
Dermal
Dermal melasma is a skin condition characterized by brown to gray patches of discoloration on the skin's surface, typically in facial areas that receive frequent or prolonged exposure to sunlight. The best treatments for melasma include preventative measures such as avoiding excessive sun exposure, proper sunscreen use, wearing protective clothing and eating a healthy diet. For more severe cases, chemical peels and laser therapy are effective treatments designed to help break down pigment into smaller particles that can be reabsorbed by the body. With early intervention, professional treatment, and following recommended lifestyle changes, many people with dermal melasma can regain their glowing complexion.
Mixed
Mixed melasma is a common skin condition that combines hyper and hypo-pigmentation, creating a marbled complexion. It’s most commonly seen in areas of the body frequently exposed to the sun including the face, arms, and neck. Treatment for mixed melasma often includes topical corticosteroids and sunscreen, with some cases also requiring laser therapy such as Q-Switched Nd YAG laser treatments or chemical peels. Your healthcare professional can recommend the best course of treatment depending on your individual needs. With early detection and proactive treatment, it is possible to improve symptoms of mixed melasma with long-lasting results.
What Causes Melasma
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation caused by hormonal changes, UV radiation exposure from the sun, and even genetics. In contrast to postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, it isn’t necessarily triggered by skin damage or irritation related to acne, eczema, or bug bites - though some irritations may also contribute.
Sun exposure
Sun exposure is a primary contributing factor to melasma. When melanin in our skin cells is overstimulated by UV rays, pigment production increases and causes these darkened patches to appear. Therefore, it is important for those susceptible to developing melasma to take preventative measures against exposure to direct sunlight, such as wearing protective clothing or sunscreen with a high SPF rating when out in the sun for extended periods.
Hormonal changes
The American Academy of Dermatology reveals that most people with melasma are female. Nicknamed “the mask of pregnancy,” this skin condition is not exclusive to expectant mothers. Still, it can additionally arise from oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapies due to heightened estrogen and progesterone levels, which stimulate the production of melanin pigment.
Genetics
Researchers believe genetic factors, including family history, hormonal make-up, and racial background, can all contribute to your predisposition for melasma. According to studies, people with a history of melasma in their families are more likely to develop the condition. Studies have shown that melasma has been connected to ethnicity in some cases, with those with more melanin in their skin being much more susceptible.
Skin irritation
Skin irritation is a trigger for the development of melasma. Some cases can be attributed to an inflammatory response on the skin due to using certain facial products and harsh soaps. When an irritating agent is applied to the skin, it stimulates the production of melanocyte-stimulating hormones by the endocrine system, which then signals to the melanocytes in our skin, increasing melanin production. This occurs as a natural protective mechanism against further irritation. The dark patches and spots we identify as melasma are ultimately caused by this overproduction of pigmentation.
Procedures That Remedy Melasma
Typically, chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion serve as potential remedies for melasma. Chemical peels help by removing the surface layers of skin, which aids in restoring the healthy skin below it. Laser therapy utilizes lasers to target maligned therapeutic areas with heat energy and can help reduce the appearance of dark patches. Microdermabrasion techniques use abrasion tools that delicately remove damaged skin cells while promoting collagen production and improving texture and tone.
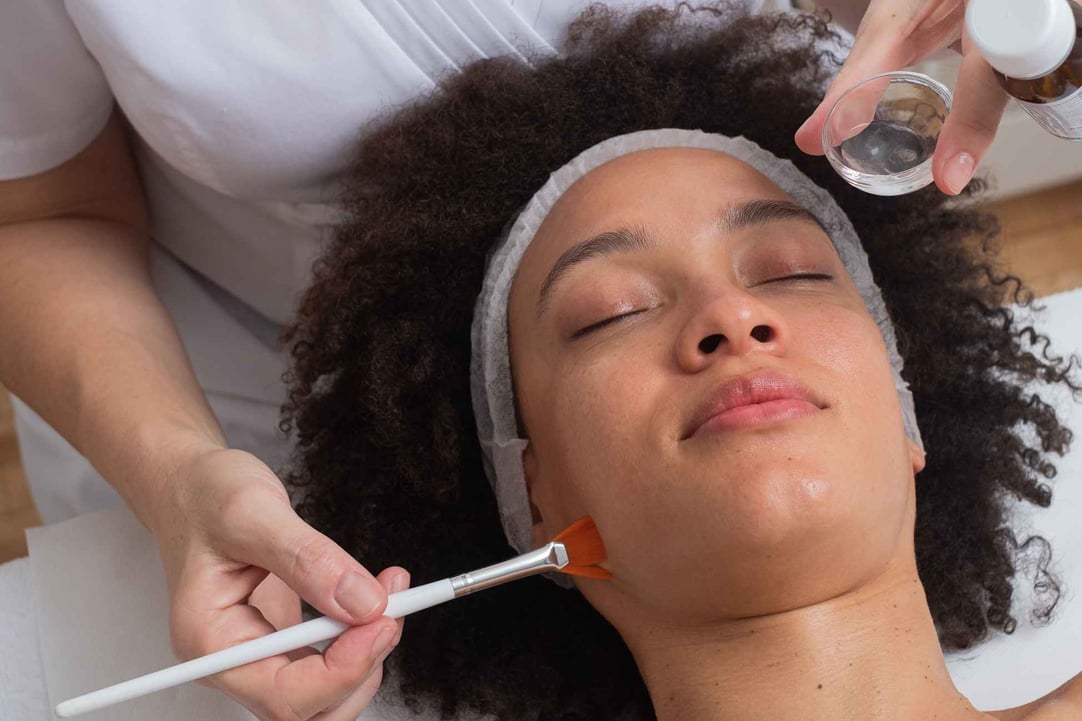
Chemical peels
Find doctors who offer Chemical PeelChemical peels are a popular method used to help reduce the appearance of melasma. The solution used in the chemical peel exfoliates the dark, blotchy patches of skin and stimulates cell turnover to improve pigmentation. As the new, healthy cells are produced, they replace old, damaged cells that contribute to an uneven complexion.
Microdermabrasion
Find doctors who offer MicrodermabrasionMicrodermabrasion has emerged as a remedy for melasma. During treatment, the top layer of your skin is mechanically exfoliated with tiny crystals that are vacuumed up along with dead skin cells. This process helps brighten the complexion, reduce hyperpigmentation related to melasma, and stimulate collagen and elastin production.
Laser therapy
Find doctors who offer Laser Skin ResurfacingLaser therapy is a safe, effective, and non-invasive remedy for melasma. This procedure uses an intense beam of light energy to target and specifically penetrate the affected skin areas. Doing this removes thin layers of damaged and discolored skin, replacing them with new skin cells stimulated by its action. This promotes consistent texture and tone in the treated area while minimizing discoloration tendencies characteristic of melasma.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Melasma permanent?
While melasma can cause emotional distress due to its appearance, it can be effectively managed with treatment. Fortunately, there is some good news regarding melasma. While it isn’t curable, treatments such as laser therapy, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion have been shown to lighten the appearance of patches significantly. With consistent use of these treatments and with protection from sun exposure by wearing sunscreen and hats, most people can manage their melasma and see positive results in a relatively short period. Regardless of severity, it’s important for those affected by melasma to remember that this is a highly manageable condition with long-term success rates in reducing the appearance of blotchy pigmentation and enhancing the complexion.
Can Melasma be prevented?
Protecting your skin from the sun is important to maintain healthy-looking skin and can help reduce the risk of developing melasma. Using sunscreen when you're outdoors and SPF- rated clothing and hats is essential. Avoid using cosmetics or skin care products that may irritate your skin to reduce any chance of flare-ups or pigmentation issues caused by hormones. Proper preventative measures can greatly minimize the risk of developing melasma.
Does Melasma only affect women?
Although melasma does affect men as well as women, women are overwhelmingly more prone to melasma than men, with the American Academy of Dermatology citing 90% prevalence among females. Commonly referred to as “the mask of pregnancy,” pregnant women often experience melanin overproduction due to their elevated estrogen and progesterone levels. This skin condition can affect non-pregnant women on birth control pills or taking hormone replacement therapy.
What are some lifestyle changes that can help improve Melasma?
Making healthy lifestyle choices can be an effective way to manage melasma. Above all, it is important to protect the skin from sun exposure by wearing sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and avoiding direct sunlight for longer periods. It is beneficial to wear sunscreen even on cloudy days, as irritation caused by ultraviolet rays can worsen melasma. Additionally, topical treatments containing natural ingredients like liquorice, aloe vera, or turmeric can be beneficial in lightening the affected areas and making melasma less noticeable. Moreover, eating a balanced diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, including leafy greens and beta-carotene, can help illuminate skin tone while providing a healthy dose of vitamins and minerals. However, talking to a healthcare professional about treatment options may be the best course of action if the issue persists.